To be a valuable global supplier
for metallic honeycombs and turbine parts
Release time:2025-06-19
Catalytic converters play a crucial role in reducing vehicle emissions, and the choice of substrate material significantly impacts their performance. metal substrate and ceramic substrates are the two primary options, each with distinct advantages in terms of thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and weight. This article explores these properties to highlight their suitability for catalytic converter applications.
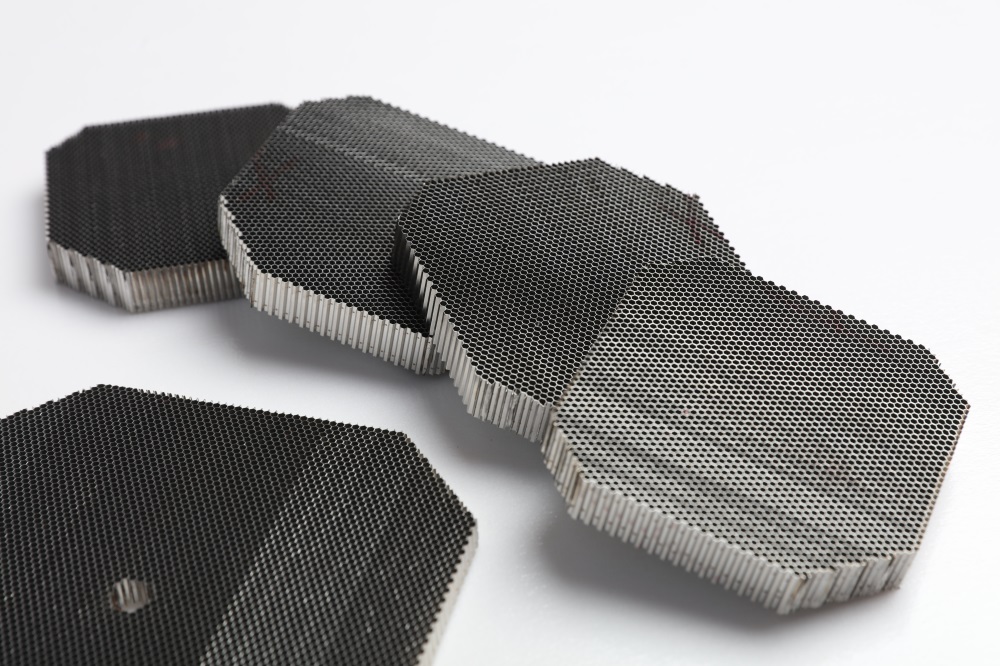
metal substrate: metal substrate, typically made of stainless steel or aluminum, exhibit high thermal conductivity. This property allows rapid heat transfer, enabling faster catalyst light-off (activation) and improved cold-start performance. The efficient heat dissipation also reduces thermal stress, enhancing durability.
Ceramic Substrates (Cordierite): Ceramic substrates, commonly composed of cordierite, have lower thermal conductivity compared to metals. While they provide good insulation, slower heat transfer can delay catalyst activation. However, their thermal shock resistance makes them suitable for high-temperature applications.
metal substrate: metal substrate offer superior mechanical strength and structural integrity, making them resistant to vibration and impact. Their ductility allows for flexible designs, including thin-walled structures that maximize surface area for catalytic reactions.
Ceramic Substrates: Ceramic substrates are brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. Although advancements in material engineering have improved their durability, they remain less robust than metal counterparts, particularly in high-vibration environments.
metal substrate: metal substrate are generally lighter than ceramic alternatives, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction. Their thin-wall construction further enhances weight efficiency without compromising strength.
Ceramic Substrates: Ceramic substrates are denser and heavier, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency. However, their high surface area-to-volume ratio compensates for the weight disadvantage in some applications.
While ceramic substrates dominate the market due to cost-effectiveness and thermal shock resistance, metal substrate for catalytic converters offer superior thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and lightweight benefits. The choice between the two depends on specific application requirements, balancing performance, durability, and weight considerations.