To be a valuable global supplier
for metallic honeycombs and turbine parts
Release time:2025-12-20
Honeycomb straightener are used to stabilize exhaust flow upstream of catalytic converters and aftertreatment units in diesel and gasoline vehicles. Typical positions include turbine outlet sections and catalyst inlet zones where swirl and velocity imbalance are present.
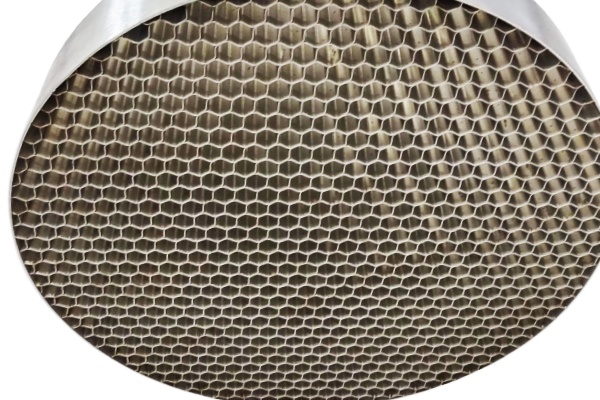
Engine exhaust flow is non-uniform. Swirl, separation, and local high-velocity regions occur depending on manifold design and turbo geometry. The honeycomb straightener aligns flow through straight parallel channels. No chemical interaction. No emission conversion function.
In gasoline systems, uneven inlet flow causes temperature gradients on the catalyst face, mainly during cold start and transient load conditions. Flow straightening improves face velocity distribution and reduces local thermal stress on the substrate.
Diesel systems operate with higher exhaust mass flow and lower tolerance for pressure increase. Honeycomb straightener for diesel applications use lower cell density and thin walls to limit back pressure. Uniform inlet flow improves DOC and SCR reaction consistency and slows uneven catalyst aging.
Metallic honeycomb straightener, typically FeCrAl-based, tolerate vibration, thermal cycling, and high exhaust temperature. Fast heat transfer. Stable geometry. Ceramic straighteners are applied where vibration is limited and thermal gradients are lower.
Cell size selection is based on exhaust velocity, available length, and acceptable pressure loss. Smaller cells provide stronger flow alignment. Larger cells reduce restriction. No universal configuration.
The Honeycomb straightener is a flow control component. Function is limited to flow stabilization and catalyst protection under operating conditions.