To be a valuable global supplier
for metallic honeycombs and turbine parts
Release time:2025-10-13
The DOC metal substrate plays a central role in modern exhaust aftertreatment systems, converting harmful gases into less toxic emissions. Behind its efficiency lies a carefully engineered production process where each step determines the substrate’s durability, surface activity, and flow performance. Understanding how a DOC metal substrate is made reveals why it is essential for reliable catalytic conversion.
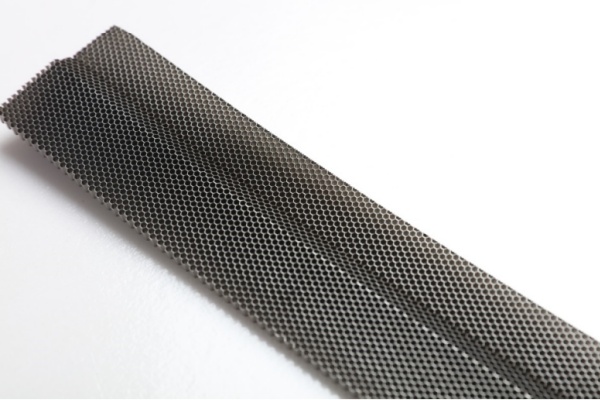
The process begins with the forming of metal foils, usually made from high-temperature resistant alloys. These thin strips must maintain uniform thickness and smooth surfaces to ensure consistent gas flow in the final product. Any imperfection at this stage could cause uneven coating or localized thermal stress later on.
Once the foils are prepared, the honeycomb rolling process starts. The metal strips are corrugated and then tightly rolled to form a cylindrical or oval honeycomb structure. This structure provides a large surface area for the catalyst while allowing exhaust gases to pass through smoothly. The geometry of the DOC metal substrate is crucial—it directly affects the flow resistance and contact time between gases and the catalytic surface.
After the honeycomb body is formed, welding secures its structure. The welding must be precise and clean to prevent distortion or weak points under high exhaust pressure. Skilled control at this stage ensures the mechanical stability of the DOC metal substrate, even under continuous temperature cycling.
Next comes the coating process, where the substrate is dipped or sprayed with a slurry containing catalytic components and binding agents. This coating layer is the heart of the DOC metal substrate, enabling oxidation reactions that reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. Uniform coating distribution ensures consistent catalytic activity across all channels.
Finally, the coated substrate undergoes drying and calcination. This step removes moisture and solidifies the coating onto the metal surface. Controlled heating strengthens the adhesion between the coating and metal foil, ensuring long-term stability in high-temperature environments.
Every phase—from foil forming to final baking—affects the DOC metal substrate’s efficiency and service life. Precision manufacturing not only improves catalytic performance but also extends durability, allowing engines to meet stringent emission standards over thousands of operating hours.
In the end, the DOC metal substrate represents more than just a component—it embodies the integration of material science, mechanical engineering, and environmental innovation. Each roll of foil, each weld, and each coating layer contributes to a cleaner and more efficient exhaust system.