To be a valuable global supplier
for metallic honeycombs and turbine parts
Release time:2025-07-21
Waveguide windows serve as critical components in modern electronic systems where both ventilation and electromagnetic shielding are required. These specialized structures effectively suppress electromagnetic leakage while maintaining adequate airflow, with their performance primarily determined by cut-off efficiency - the ability to block electromagnetic waves below a designed threshold frequency.
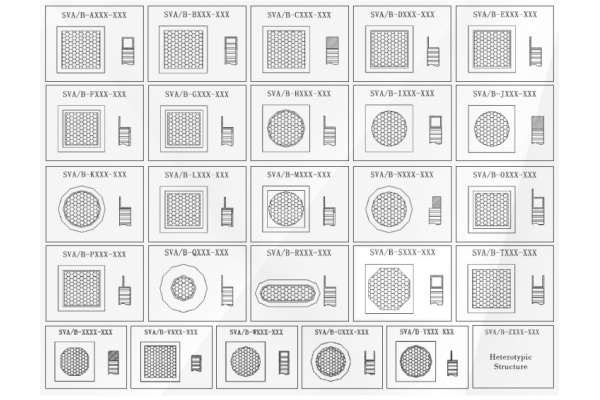
The cut-off efficiency of waveguide windows fundamentally depends on their geometric parameters. For rectangular waveguide structures, the cut-off frequency inversely correlates with the waveguide width. Precise dimensional engineering ensures complete reflection or attenuation of target frequency bands, preventing electromagnetic leakage. A 5mm honeycomb configuration, for instance, can effectively block electromagnetic waves below 30GHz.
The honeycomb or grid-like internal structure features channels significantly smaller than the target wavelength. When electromagnetic waves enter below the cut-off frequency, the waveguide fails to establish proper propagation modes, forcing wave reflection or attenuation. This physical confinement mechanism provides the foundation for high cut-off efficiency.
High-conductivity materials like aluminum and copper form the basis of waveguide windows, often with nickel-plated surfaces for improved conductivity. These materials minimize reflection losses at structural interfaces, directly boosting cut-off efficiency while ensuring long-term durability against corrosion.
Advanced designs incorporate multiple shielding layers, combining metal meshes with waveguide structures. This hybrid approach addresses different frequency ranges simultaneously - the mesh filters lower frequencies while the waveguide handles higher frequencies - resulting in superior overall cut-off efficiency across broader spectra.
Proper installation requires conductive sealing materials (conductive rubber or metal springs) at mounting interfaces, complemented by robust grounding. These measures maintain electromagnetic integrity by eliminating leakage paths and compensating for mechanical or thermal stresses that might otherwise degrade cut-off efficiency over time.
Waveguide windows achieve exceptional electromagnetic leakage prevention through coordinated optimization of structural parameters, material properties, multilayer configurations, and interface treatments - all contributing to maximized cut-off efficiency. As electronic systems continue to advance, further improvements in waveguide window technology will focus on extending frequency coverage while maintaining ventilation performance and structural reliability.